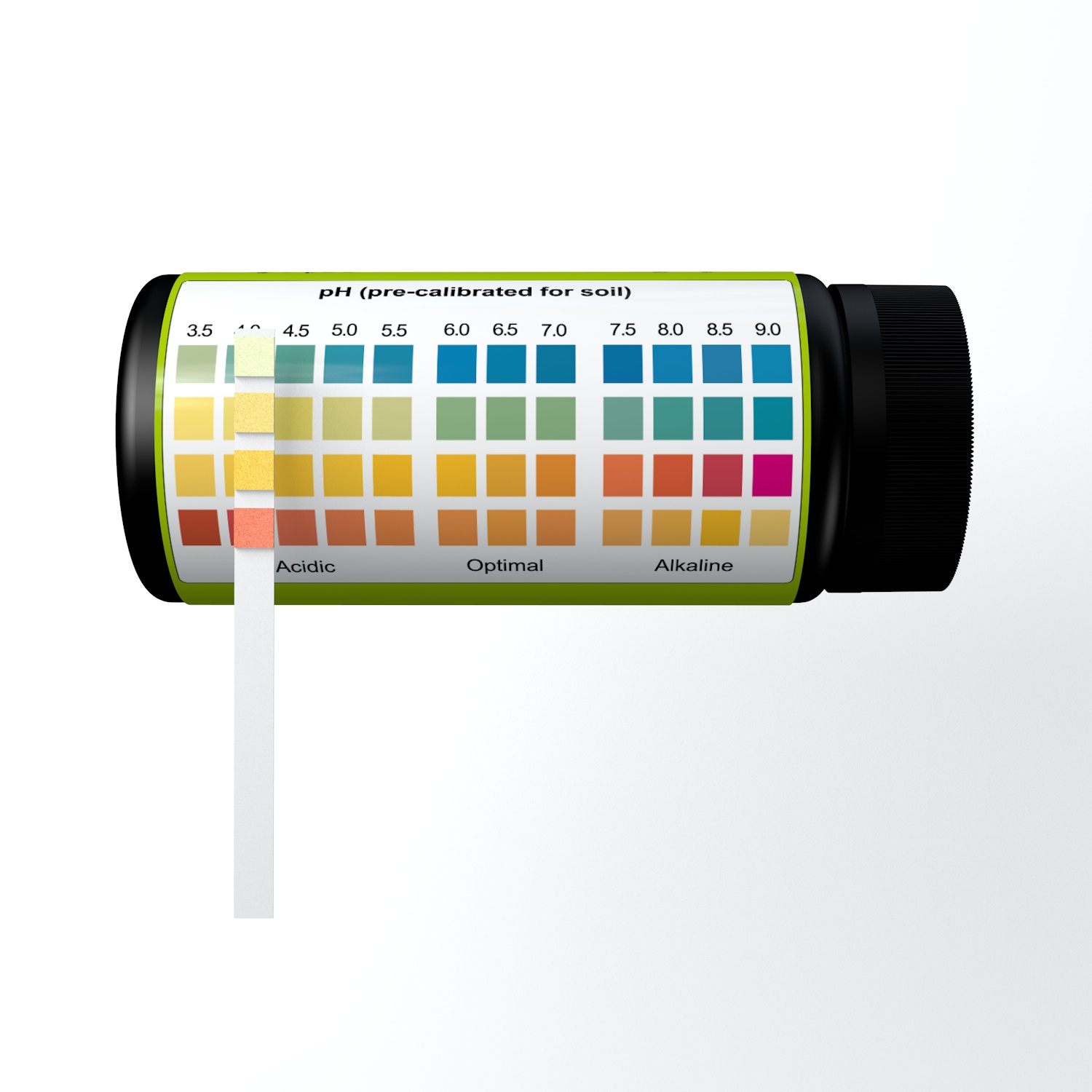
Soil Ph Indicator Test Kit Ph Strips 3.5-9.0
Brand :TSTCHECK
Product origin :Changchun, CN
Delivery time :3-20 days
Supply capacity :300,000 bottles
Soil Ph Indicator Test Kit Ph Strips 3.5-9.0 is developed and manufactured by Jilin Test Bio-Electron Co., Ltd. The testing products have been successful in the world market for many years.
As rapid and affordable test products, Soil Ph Indicator Test Kit Ph Strips 3.5-9.0 adopts new chromogenic agents and use highly sensitive chromogenic reaction activators to perform semi-quantitative analysis of pH level.
Using superior technology, delivering accurate results, strong anti-pollution ability, and rapid diagnoses of pH level within 100 seconds, Soil Ph Indicator Test Kit Ph Strips 3.5-9.0 is essential to maintaining Planting and Garden.
Soil pH Test Strips: A Comprehensive Guide
1. Introduction
2. Understanding Soil pH
2.1 The Significance of Soil pH for Plant Growth
Nutrient Availability: Different nutrients in the soil are more or less available to plants depending on the soil's pH. For example, in acidic soils (pH less than 7), iron, manganese, and aluminum are more soluble and can be more easily taken up by plants. However, if the soil is too acidic, these elements can reach toxic levels for some plants. On the other hand, in alkaline soils (pH greater than 7), nutrients like phosphorus, iron, and zinc can become less available, leading to nutrient deficiencies in plants.
Microbial Activity: The soil is teeming with microorganisms that play a crucial role in processes such as decomposition of organic matter and nitrogen fixation. These microorganisms have specific pH preferences. For instance, most beneficial soil bacteria thrive in a slightly acidic to neutral pH range. An incorrect pH can inhibit their activity, which in turn affects the soil's fertility and the plant's ability to obtain nutrients.
2.2 Natural Factors Affecting Soil pH
Parent Material: The type of rock and minerals from which the soil is formed (parent material) has a significant influence on soil pH. Soils derived from limestone, which is rich in calcium carbonate, tend to be alkaline. In contrast, soils formed from granite or sandstone, which are low in bases, are often more acidic.
Climate and Rainfall: Regions with high rainfall tend to have more acidic soils. This is because rainwater is slightly acidic (due to dissolved carbon dioxide from the atmosphere), and over time, it can leach basic cations like calcium, magnesium, and potassium from the soil, making it more acidic. In arid regions, evaporation can cause the accumulation of salts in the soil, which can increase soil alkalinity.
3. How Soil pH Test Strips Work
3.1 The Components of Soil pH Test Strips
Reagent - Impregnated Paper: The core of a soil pH test strip is the reagent - impregnated paper. This paper is treated with specific chemical compounds that are sensitive to the hydrogen ion concentration in the soil solution. The most common reagents used in soil pH test strips are indicators such as bromothymol blue, phenolphthalein, or a combination of several indicators.
Base Material: The reagent - impregnated paper is attached to a sturdy base material, usually a type of plastic or thick paper. The base material provides support to the test strip and makes it easy to handle during the testing process.
3.2 The Chemical Reaction Behind pH Detection
3.3 Color - Comparison and pH Determination
4. Types of Soil pH Test Strips
4.1 General - Purpose Soil pH Test Strips
4.2 Specialized Soil pH Test Strips
Acidic - Soil - Specific Test Strips: Some plants, such as blueberries, azaleas, and rhododendrons, prefer acidic soils. Acidic - soil - specific test strips are designed to provide more accurate readings in the lower pH range, typically from 3 to 6. These test strips are more sensitive to the small changes in pH that are relevant for acid - loving plants. They are useful for gardeners who are growing these specific types of plants and need to closely monitor and maintain the acidic soil conditions.
Alkaline - Soil - Specific Test Strips: In regions with naturally alkaline soils or for plants that thrive in alkaline conditions, alkaline - soil - specific test strips are available. These test strips focus on the higher pH range, usually from 7 to 10. They are beneficial for farmers in arid or semi - arid regions where the soil is often alkaline, as well as for gardeners growing plants like lilacs or clematis, which prefer alkaline soil.
4.3 Combined Test Strips
5. Using Soil Test Kit pH and pH Test Strips Effectively
5.1 Sample Collection
Proper Sampling Technique: To obtain accurate results when using soil pH test strips or a soil test kit pH, proper sample collection is crucial. For gardeners, samples should be taken from different areas of the garden or planting bed. Use a clean trowel or soil sampler to collect soil from a depth of about 6 - 8 inches. Mix the soil samples thoroughly in a clean container to create a composite sample. This composite sample will give a more representative reading of the overall soil pH in the area.
Avoiding Contamination: It's important to avoid contaminating the soil sample. Do not collect soil near sources of pollution such as roads (where there may be vehicle - related contaminants), industrial areas, or areas treated with chemicals. Also, make sure the sampling tools are clean to prevent introducing foreign substances that could affect the pH measurement.
5.2 Testing Procedure
Using Soil pH Test Strips: If using soil pH test strips, first moisten the soil sample slightly (but not too wet, as overly saturated soil can affect the accuracy). Then, insert the test strip into the soil or, preferably, into a soil - water mixture (made by mixing a small amount of soil with distilled water). Wait for the recommended time, usually a few seconds to a minute, for the color change to occur. Compare the color of the test strip with the color - comparison chart to determine the pH value.
Soil Test Kit pH: A soil test kit pH may have a more elaborate testing procedure. It may involve using a test tube, adding a specific amount of soil and a reagent solution, shaking the mixture, and then observing the color change in the test tube. Some kits may also require the use of a color - matching device for more accurate readings. Follow the instructions provided with the kit carefully for the best results.
5.3 Frequency of Testing
Initial Assessment: When starting a new garden or agricultural project, it's advisable to test the soil pH initially to get a baseline reading. This will help in determining the appropriate plants to grow and any necessary soil amendments.
Regular Monitoring: After the initial assessment, the frequency of soil pH testing depends on various factors. In a garden, it may be sufficient to test the soil pH once every 1 - 2 years. However, in agricultural fields where intensive cropping is practiced, or in areas where there have been significant changes such as the addition of large amounts of organic matter or the use of lime or sulfur for soil pH adjustment, more frequent testing (annually or even quarterly) may be necessary to monitor the effectiveness of the management practices.
6. Advantages of Soil pH Test Strips
6.1 Simplicity and Ease of Use
6.2 Quick Results
6.3 Cost - Effectiveness
6.4 Portability
7. Applications of Soil pH Test Strips and pH Indicators
7.1 Home Gardening
Plant Selection: Home gardeners can use soil pH test strips to determine the pH of their soil and then select plants that are well - suited to the soil's pH. For example, if the soil is acidic, they can choose acid - loving plants like hydrangeas, which change color depending on the soil pH. If the soil is alkaline, plants like daylilies or yarrow can be a good choice.
Soil Amendment Planning: Based on the pH test results, gardeners can plan soil amendments. If the soil is too acidic, adding lime can raise the pH. If it's too alkaline, sulfur or peat moss can be added to lower the pH. Test strips can be used to monitor the effectiveness of these amendments over time.
7.2 Agriculture
Crop Yield Optimization: In agriculture, soil pH has a direct impact on crop yields. Different crops have different pH preferences. For example, wheat and barley generally prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH, while soybeans can tolerate a wider pH range. By using soil pH test strips or a soil test kit pH, farmers can adjust the soil pH to optimize crop growth and increase yields.
Fertilizer Management: Soil pH affects the availability of fertilizers. In acidic soils, some fertilizers may not be as effective as in neutral or alkaline soils. By knowing the soil pH, farmers can choose the right type and amount of fertilizer to apply, reducing waste and increasing the efficiency of fertilizer use.
7.3 Environmental Monitoring
Soil Health Assessment: Environmentalists use soil pH test strips and pH indicators to assess the health of natural ecosystems. Changes in soil pH can indicate pollution, such as acid rain deposition in forests or the impact of industrial activities on nearby soils. Monitoring soil pH over time can help in understanding the long - term effects of environmental changes on soil quality.
Wetland Restoration: In wetland restoration projects, soil pH is an important factor. Wetlands have specific pH requirements for the growth of native plants. By testing the soil pH using test strips, restoration practitioners can ensure that the soil conditions are suitable for the establishment of wetland - specific plant species.
8. Comparing Soil pH Test Strips with Other Soil pH Testing Methods
8.1 Laboratory - Based Analyses
Accuracy and Precision: Laboratory - based methods, such as using a pH meter in a laboratory setting, are generally more accurate and precise than soil pH test strips. The pH meter can provide a digital reading with a high level of precision, often up to two decimal places. However, this high accuracy comes at a cost. Laboratory tests require expensive equipment, proper calibration, and trained personnel to operate the equipment and interpret the results.
Complexity and Time - Consuming: Laboratory - based analyses are complex and time - consuming. The soil sample needs to be carefully prepared, transported to the laboratory, and then analyzed using the appropriate equipment. The entire process can take days or even weeks, depending on the laboratory's workload. In contrast, soil pH test strips can provide results within minutes, making them more suitable for quick, on - site assessments.
8.2 Electronic Soil pH Meters
Initial Investment: Electronic soil pH meters are another option for measuring soil pH. These meters can be relatively accurate and can be used in the field. However, they require an initial investment in the meter itself, which can be costly. Additionally, they need to be calibrated regularly, and the calibration process can be somewhat complex.
Limitations in Certain Soil Conditions: Electronic soil pH meters may have limitations in certain soil conditions. For example, in soils with high salt content or in very dry soils, the readings may not be as accurate. Soil pH test strips, on the other hand, can be used in a wider range of soil conditions and are not as affected by factors such as soil texture or salt content in the same way as electronic meters.
9. Storage and Shelf - Life of Soil pH Test Strips
9.1 Storage Conditions
9.2 Shelf - Life
10. Conclusion
Factory. We speicalize in producing water test strips for years....more
-
Download
- Category.pdf